HIV and AIDS: All You Need to Know About the Virus

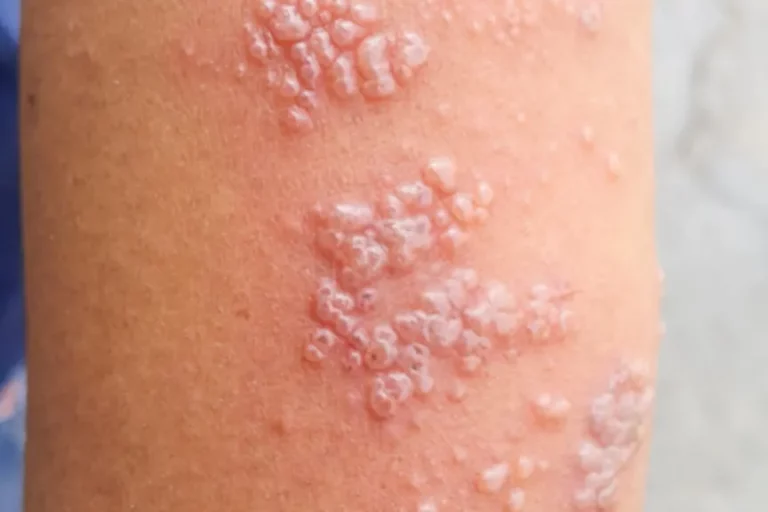
HIV or thehuman immunodeficiency virus, is a virus that attacks cells that help the body fight infection. As a result, a person infected with the virus is more likely to contract additional infections and diseases. It transmits through intimate contact with certain bodily fluids of a person who has HIV. Most frequently through sexual activity that is not safe. Sexual activity that does not involve the use of a condom or HIV medication. To prevent or treat HIV), or through the sharing of injection drug equipment..
Monkeypox: What is it and how do you catch it?
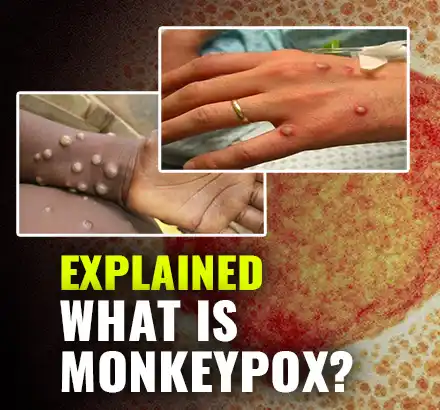
Monkeypox is a rare disease that is caused by infection with monkeypox virus. Monkeypox virus belongs to theOrthopoxvirusgenus in the familyPoxviridae. TheOrthopoxvirusgenus also includes variola virus (which causes smallpox), vaccinia virus (used in the smallpox vaccine), and cowpox virus..
Rubella: Causes and Treatments
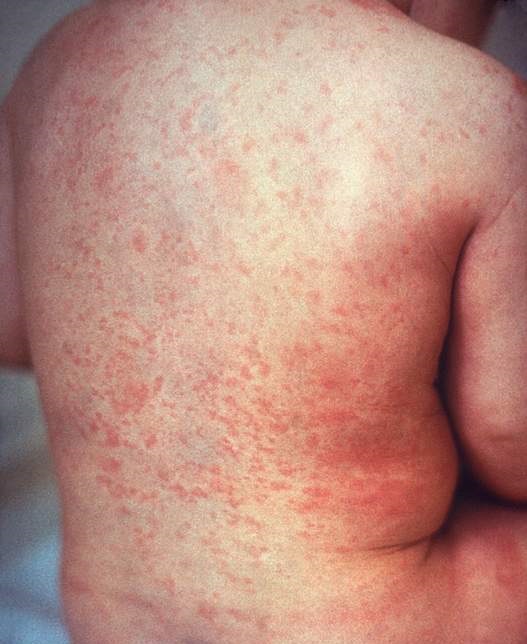
Rubella is a contagious viral infection characterized by a characteristic red rash. Also, it is a skin and lymph node infection that affects the majority of people. It’s also known as three-day measles or German measles. While most people will experience very minor symptoms or none at all, it can have catastrophic consequences for unborn children whose mothers become infected during pregnancy..
DENGUE FEVER: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENTS
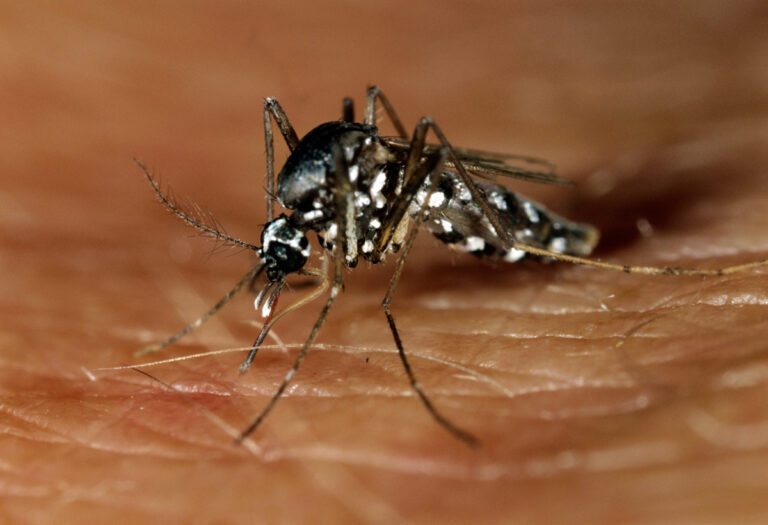

Every year, millions of people become infected with dengue. Southeast Asia, the western Pacific islands, Latin America, and Africa are the most affected by dengue fever. However, the disease has spread to new areas, including local outbreaks in Europe and the southern United States..
Measles: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
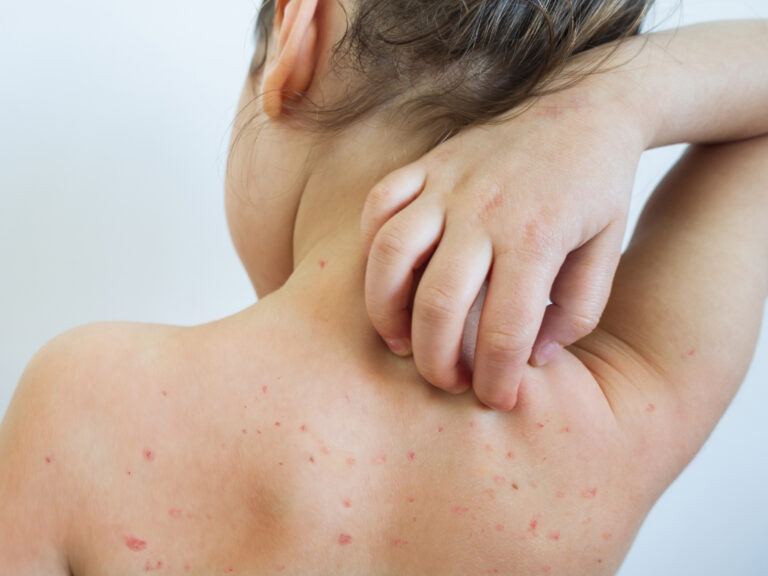
The rubeola virus causes measles. It spreads through intimate contact with an infected person or airborne droplets. This type of virus can live up to two hours on surfaces or in the air, infecting 90% of individuals infected. This type of disease is a highly contagious disease that can be fatal. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 1-3 out of 1,000 cases of measles are deadly. Unvaccination is the main risk factor for measles. Young children, people with weakened immune systems, and pregnant women are more susceptible to complications from measles infection..