Sleep Apnea: Types, Symptoms, and Treatments
Author: Giselle Robel
Giselle Robel
Category: Health
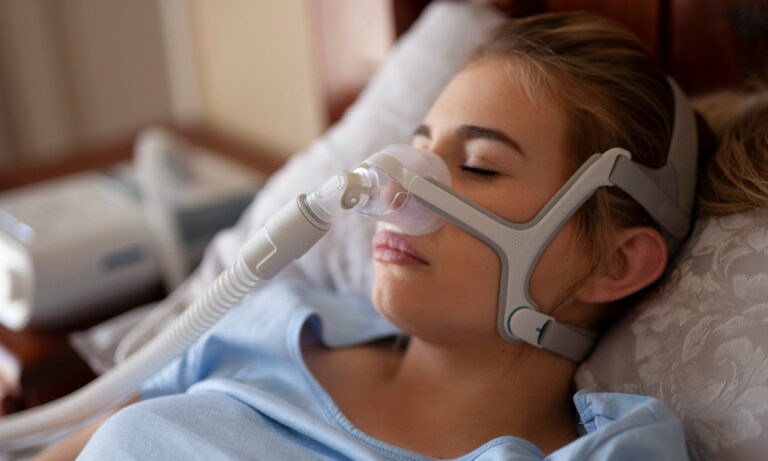
Sleep apnea is a severe sleeping disorder that happens when a person breathing stops suddenly during sleep. People with untreated sleep apnea stop breathing repetitiously during their sleep, sometimes hundreds of times during the night.
It is a severe sleeping disorder in which breathing repeatedly stops for 10 seconds then starts again. Causing loud snoring and daytime tiredness, even with a night full of sleep. Such matter can also lead to more severe health issues, such as high blood pressure and heart trouble. This disorder results in less oxygen in the blood and can briefly awaken sleepers throughout the night. It can affect people of all ages, particularly people over the age of 50 and those with overweight problems.
Untreated sleep apnea can also be responsible for job impairment, work-related accidents, and motor vehicle crashes.

The Main Types of Sleep Apnea are:
¢ Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is more common among them. Occurs as repetitive episodes of complete or partial upper airway blockage during sleep. During an apneic episode, the diaphragm and chest muscles work harder as the pressure increases to open the airway. Breathing usually resumes with a loud gasp or body jerk. These episodes can interfere with sound sleep, reduce the flow of oxygen to vital organs, and cause heart rhythm irregularities.
¢ Central S leep A pnea( CSA), which happens when your brain doesn’t send proper signals to the brain fails to signal the muscles to breathe due to instability in the respiratory control center. Central sleep apnea is related to the function of the central nervous system.
¢ Complex sleep apnea syndrome occurs when someone has both obstructive sleep apnea and central sleep apnea.
Sleep Apnea stops breathing suddenly
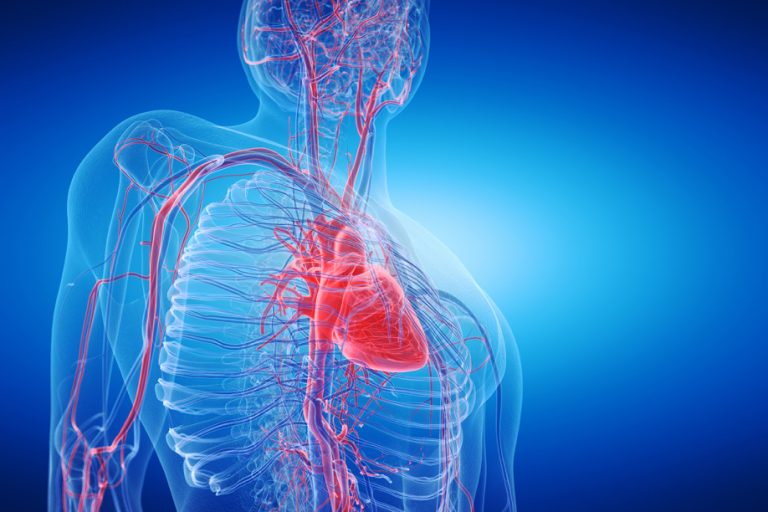
The heart rate drops when breathing suddenly stops. Then, your involuntary reflexes cause you to startle awake at the end of that period of not breathing. When this occurs, your heart rate tends to accelerate quickly and your blood pressure rises.
For example, your blood pressure tends to go up, your heart walls thicken due to increased workload, and the structure of your heart changes. It tends to become stiffer and less flexible because there are more fibrous cells growing in between the muscle cells.
Sleep Apnea S ymptoms An d C auses
In general, the soft tissues behind the throat collapse during sleep is common to people with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Central sleep apnea is usually in patients with central nervous system dysfunction. It is also common in patients with heart failure and other forms of heart, kidney, or lung disease. those affected have no sleep complaints.
People with CSA more often report recurrent awakenings or insomnia, although they may also experience a choking or gasping sensation upon awakening.
Diagnosis
If your doctor determines that you have symptoms suggestive of sleep apnea, you may be asked to have a sleep evaluation or may order an overnight sleep study to objectively evaluate.
Treatments:
¢ Overweight persons can benefit from losing weight. However, losing weight can be difficult to do due to increased appetite and metabolic changes.
¢ Individuals with OSA should avoid the use of alcohol and certain sleeping pills, which make the airway more likely to collapse while sleeping and prolong the apneic periods.
¢ In some patients with mild OSA breathing pauses occur only when they sleep on their backs. In such cases, using a wedge pillow or other devices that help them sleep in a side position may help.
¢ People with sinus problems or nasal congestion should use nasal sprays or breathing strips to reduce snoring and improve airflow for more comfortable nighttime breathing. Avoiding sleep deprivation is important for all patients with sleep disorders.
Additional Treatments
Mechanical therapy: Positive Airway Pressure (PAP) therapy is the preferred initial treatment for most people with obstructive sleep apnea.
Mandibular advancement devices: These are devices for patients with mild to moderate OSA.
Hypoglossal nerve stimulator: A stimulator is implanted under the skin on the right side of the chest with electrodes tunneled under the skin to the hypoglossal nerve in the neck and intercostal muscles (between two ribs) in the chest. The device is turned on at bedtime with remote control. With each breath, the hypoglossal nerve is stimulated, the tongue moves forward out of the airway and the airway is opened.
Surgery: Surgical procedures may help people with OSA and others who snore but don't have this problem. Among the many types of surgeries done are outpatient procedures. Surgery is for people who have excessive or malformed tissue obstructing airflow through the nose or throat.
What are the effects?
If left untreated, it can result in several health problems, including hypertension, stroke, arrhythmias, cardiomyopathy (enlargement of the muscle tissue of the heart), heart failure, diabetes, obesity, and heart attacks.
Sleep apnea can likely cause arrhythmias and heart failure because you tend to have higher blood pressure.