Vaginitis – Types, Symptoms, and Prevention
Author: Giselle Robel
Giselle Robel
Category: Health
Vaginitis is an inflammation of the vagina that can result in discharge, itching, and pain.
The cause is usually a change in the normal balance of vaginal bacteria or an infection.
And, in addition to that, reduced estrogen levels after menopause and some skin disorders can cause vaginitis.
Most Common Types of Vaginitis
- Bacterial vaginosis – resulting from a change of the normal bacteria found in your vagina to overgrowth of other organisms
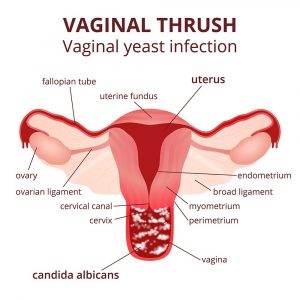
- Yeast infections – are usually caused by a naturally developing fungus called Candida albicans
- Trichomoniasis – is caused by a tiny one-celled parasite named Trichomonas vaginali and is commonly transmitted by sexual intercourse
Symptoms of Vaginitis
Vaginitis signs and symptoms can include:
- Change in color, odor or amount of discharge from your vagina
- Vaginal itching or irritation
- And pain during intercourse
- Painful urination
- Light vaginal bleeding or spotting
If you have a vaginal discharge, which many women don’t, the characteristics of the discharge might tell the type of vaginitis you have.
Examples include:
- Bacterial vaginosis
- Burning feeling when you pee
- Fishy smell that gets stronger after sex
- Itching
- Thin white, gray, or green discharge
- Yeast infection
- Itching and irritation in the vagina and vulva
- A burning sensation, especially during intercourse or while urinating
- Redness and swelling of the vulva
- Vaginal pain and soreness
- Vaginal rash
- Thick, white, odor-free vaginal discharge with a cottage cheese appearance
- Watery vaginal discharge
- Trichomoniasis
Causes
The cause depends on what type of vaginitis you have:
- Bacterial vaginosis – is the most common cause of vaginitis resulting from a change of the normal bacteria found in your vagina.
- It’s an overgrowth of one of several other organisms.
- Usually, bacteria normally found in the vagina (lactobacilli) are outnumbered by other bacteria (anaerobes) in your vagina.
- If anaerobic bacteria become too numerous, they upset the balance, causing bacterial vaginosis.
- This type of vaginitis seems to be linked to sexual intercourse, especially if you have multiple sex partners or a new sex partner.
- But it also occurs in women who aren’t sexually active.
- Yeast infections – these occur when there’s an overgrowth of a fungal organism called Candida Albicans in your vagina.
- Candida Albicans, also causes infections in other moist areas of your body, such as in your mouth (thrush), skin folds and nail beds.
- The fungus can also cause diaper rash.
- Trichomoniasis – this common sexually transmitted infection.
- This organism spreads during sexual intercourse with someone who has the infection.
- In men, the organism usually infects the urinary tract, but often it causes no symptoms.
- In women, trichomoniasis typically infects the vagina, and might cause the symptom.
- It can also increase a woman’s risk of getting other sexually transmitted infections.
- Noninfectious vaginitis – vaginal sprays, scrubbing, perfumed soaps, scented detergents.
- Spermicidal products may cause an allergic reaction or irritations in the vulvar and vaginal tissues.
- Foreign objects, such as tissue paper or forgotten tampons, in the vagina can also irritate vaginal tissues.
- Genitourinary syndrome of menopause(vaginal atrophy) – reduced estrogen levels after menopause or surgical.
- Removal of your ovaries can cause the vaginal lining to thin.
- Sometimes resulting in vaginal irritation, burning, and dryness.
Prevention
Good hygiene may prevent some types of vaginitis from recurring and may relieve some symptoms:
- Avoid baths, hot tubs and whirlpool spas .
- Avoid irritants – these include scented tampons, pads, douches and scented soaps.
- Rinse soap from your outer genital area after a shower, and dry the area well to prevent irritation.
- Don’t use harsh soaps, such as those with deodorant or antibacterial action, or bubble bath.
-
Wipe from front to back after using the toilet – doing so avoids spreading fecal bacteria to your vagina.
-
Don’t scrub – your vagina doesn’t require cleansing other than normal bathing.
- Repetitive scrubbing disrupts the normal organisms that reside in the vagina and can actually increase your risk of vaginal infection.
- Scrubbing won’t clear up a vaginal infection.
- Use a latex condom – both male and female latex condoms may help you avoid infections spread by sexual contact.
- Wear cotton underwear – also wear pantyhose with a cotton crotch.
- If you feel comfortable without it, skip wearing underwear to bed.
- Yeast thrives in moist environments.