Common Bone Marrow Diseases
Author: Rose Stella
Rose Stella
Category: Health

The bone marrow
The bone marrow is the soft, spongy tissue in the core of most bones. Bone marrow comes in two colors: red and yellow. Blood stem cells can produce red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets in the red bone marrow. The bone marrow is located at the sternum (middle of the chest), pelvis (hip bone), and femur (thigh bone). Various instances causes the bone marrow to malfunction, thus causing various bone marrow diseases.
The bone marrow is the spongy substance found in the core of the bones. It produces bone marrow stem cells and other components, which are then converted into blood cells. Each type of blood cell produced by the bone marrow serves a vital purpose.
- Red blood cells transport oxygen to the body’s tissues.
- Platelets help blood coagulate and so halt bleeding.
- White blood cells fight infections.
Bone marrow issues

Bone marrow diseases happen because of the imbalance formation of mature blood cells. The following are the most common types of bone marrow issues:
- Higher production of one type of cell results in a decrease in the production of the other cells.
- Cells don’t die on a regular basis thus, an increase in one cell line.
- Production of immature cells that do not mature or function properly.
- Producing fragile cells that die easily or producing a fewer number of cells
- Increased growth of the supporting fibrous tissue network leads to the formation of abnormal cells and decreased numbers of cells.
- Lack of iron makes RBC formation difficult
- Spread of other diseases to the bone marrow
Common bone marrow disease
Leukemia

Leukemia is a type of blood and bone marrow cancer. This type of cancer is characterized by the uncontrollable growth of abnormal cells. Cancer can occur in any part of the body. This fast, out-of-control growth of abnormal cells occurs in the bone marrow of leukemia patients. These abnormal cells then make their way into the blood system. Unlike other cancers, leukemia does not usually form a tumor that can be seen on imaging tests like X-rays.
There are several different types of leukemia. Some are more prevalent in children, while others are more prevalent in adults. The type of leukemia and its factors determines the treatment plan to cure the disease.
Leukemia starts during the process of developing blood cells in the bone marrow. Blood cells start to multiply and split inside the bone marrow, forming red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. However, if you have leukemia, one of these blood cell types begins to multiply rapidly and uncontrollably. These abnormal cells, known as leukemia cells, begin to colonize the space within the bone marrow. They suffocate the other normal cell types that are attempting to develop.
The type of leukemia, age and overall health, and whether or not leukemia has spread to other organs or tissues determines the remedy strategy. There are five types of treatments that are commonly used. These are chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and stem cell or bone marrow transplant.
Myeloproliferative disorders (MPD)
Chronic myeloproliferative disorders (MPD) are rare blood cancers with a wide
range of symptoms and no known cause. As a result, they can be hard to
diagnose. It is not uncommon to require years of care and treatment.
MPD happens when the bone marrow produces an abnormally large number of
deformed red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets. These build up in
your bloodstream.
These conditions are hard to cure. Usually, the doctor will focus on returning your blood cells to average levels and lowering your risk of major health problems. The type of myeloproliferative disorder a patient has determines the patient treatment stratergy. Some of the most common treatments are chemotherapy, stem cell or bone marrow transplant, phlebotomy, gene therapy, and hormone therapy.
Aplastic Anemia
Aplastic anemia is a condition in which your body does not produce sufficient new blood cells. The disease causes tiredness and makes you more vulnerable to infection and uncontrollable bleeding.
Aplastic anemia is a rare and serious condition that can strike at any age. It can happen suddenly or gradually and worsen over time. It can range from mild to severe.
The common treatment for this condition involves medication, blood transfusions, a stem cell or bone marrow transplant.
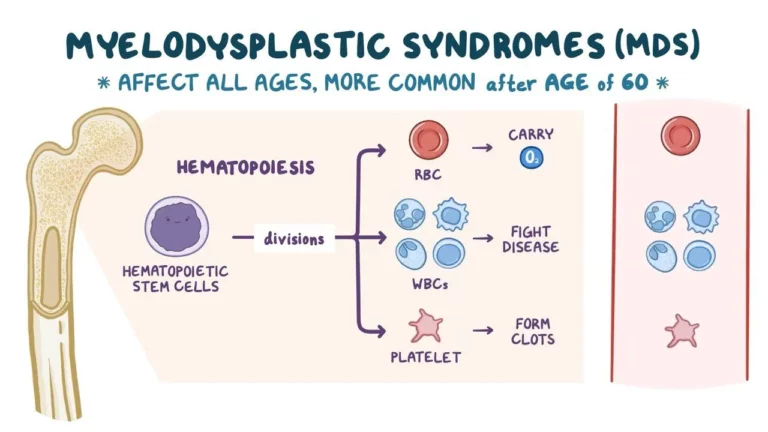
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS)
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are ailments that can happen when the bone marrow’s blood-forming cells become irregular. This results in a deficiency of one or more types of blood cells. MDS is classified as a cancer.
In MDS, several of the bone marrow cells are irregular (dysplastic) and have difficulty producing new blood cells. Many of the blood cells produced by bone marrow cells are faulty. Defective cells frequently die before normal cells, and the body also ruins some abnormal blood cells, leaving the person with an insufficient number of normal blood cells. Various cell types can be damaged, but the most common finding in MDS is a lack of red blood cells (anemia).
Myelodysplastic syndromes is classified into several types. The distinct types of blood cells heavily impacted and other aspects are the basis in classifying Myelodysplastic syndromes .
The type of MDS, MDS risk group, and other factors, as well as your age and overall health, all influence treatment. There are several methods of treatment availble to cure this disease. Doctors tailor each patient’s treatment to give them the best possibility of curing the tumor while minimizing adverse effects as much as possible.
Iron deficiency anemias

Iron deficiency anemia is a common type of anemia, defined as a lack of healthy red blood cells in the blood. Red blood cells transport oxygen to the tissues of the body.
In addition, iron deficiency anemia happens when the iron in the body is lacking. Your body cannot produce enough of a substance in red blood cells that allows them to carry oxygen if you do not have enough iron (hemoglobin). As a result, iron deficiency anemia can cause fatigue and difficulty breathing.
Iron supplementation can usually cure iron deficiency anemia. Severe cases of this disease requires diagnotic tests and treatments.