Childbirth Problem During Pregnancy
Author: Alvin
Alvin
Category: Women's Health
Tags: health, men's health, birth, abnormalities, baby, fitness

What Is Childbirth Problem?
While still in the womb, some kids suffer issues with the way their organs and body parts develop, function, or convert food to energy. These health issues refer to as childbirth problem.
There are about 4,000 different types of birth abnormalities, ranging from mild ones that may not require treatment to severe ones that cause impairments or necessitate medical or surgical intervention.
What Kinds of Birth Defects Are There?
When a baby is born with a missing or deformed body component, this is a structural birth defect. The most prevalent type of structural defect is a heart defect. Spina bifida, cleft palate, clubfoot, and congenital dislocated hip are among the others.
When a baby’s biological chemistry is abnormal, this is a metabolic birth defect. Metabolic disorders impair the body’s ability to effectively break down food to generate energy. Tay-Sachs disease, a deadly condition is affecting the central nervous system, and phenylketonuria (PKU), which affects how the body processes protein, are two examples of metabolic abnormalities.
It’s critical for anyone considering parenthood to understand that certain birth abnormalities are preventable. Taking folic acid and obtaining adequate iodine in the diet during pregnancy can help avoid certain birth abnormalities. However, it’s critical to remember that most babies born with birth abnormalities are born to two healthy parents who have no apparent health concerns or risk factors.
What Factors Contribute to Childbirth Problem?
In the majority of situations, doctors are unable to determine what caused a baby’s birth abnormality. It may be environmental (e.g., a newborn exposed to toxins or viruses while in the womb), genetic, or a mix of factors.
Environmental Determinants
If a pregnant woman has certain diseases (such as toxoplasmosis), her baby may be born with a birth defect. Other contagious diseases that might result in birth abnormalities include rubella and chickenpox (varicella). Fortunately, because so many individuals immunize against these diseases, these infections are uncommon.
Additionally, maternal alcohol misuse may result in fetal alcohol syndrome, and certain medications taken by the mother may result in birth abnormalities. (Because doctors attempt to avoid dangerous medications during pregnancy, pregnant women should inform every doctor with whom they consult that they are expecting.)
Genetic Factors of Childbirth Problem
Each cell in the body contains chromosomes, which carry genes contributing to an individual’s unique features. A child inherits one pair of chromosomes (and one pair of the genes they contain) from each parent at conception. A mistake during this procedure might result in a newborn being born with an abnormally large or small number of chromosomes or with a damaged chromosome.
Down syndrome is a well-known congenital condition caused by chromosomal abnormalities. Down syndrome occurs when a kid is born with an extra chromosome. Other genetic abnormalities occur when both parents pass on a defective gene associated with the same disease.
Additionally, an illness or deficiency might occur when only one parent carries the disease’s gene. This category covers congenital abnormalities such as achondroplasia (a type of dwarfism) and Marfan syndrome.
Finally, some boys have illnesses as a result of genes passed down only through their mothers. These abnormalities, including hemophilia and color blindness, are X-linked because the genes are on the X chromosome.
What Methods Are Used to Diagnose Childbirth Problem?
Numerous birth abnormalities can be detected even before a baby is born via prenatal testing. Prenatal tests can also assist in establishing whether a mother is suffering from an illness or another disease that could be harmful to the fetus. Knowing about a baby’s health problems in advance can assist parents and doctors in making plans.
It’s critical to keep in mind that screening simply detects the chance of a problem. Certain mothers deliver a healthy baby even though a screening test indicates the presence of a problem. If you’re pregnant, consult your doctor about any tests.
During routine newborn screenings, further birth problems. After delivery, with the parents’ consent, babies are screened for certain congenital abnormalities that require treatment. In the United States, the specific disorders for which a baby varies by state. Parents should inquire with their health care providers or the hospital nursery about the tests conducted in their state.
Parents concerned about another type of birth defect may be able to have their baby checked. They should discuss it with their health care practitioner before the baby’s birth.
Is It Possible to Prevent Childbirth Problem?
While many birth defects are unavoidable, a woman can take steps before and during pregnancy to help reduce her odds of having a kid with a birth defect.
Women should take the following precautions before pregnancy:
ensure that their vaccines are current
ascertain that they are free of sexually transmitted infections (STDs)
Before attempting to conceive, take the daily recommended dose of folic acid. Avoid needless medications and communicate with their doctor about any medications they are currently using.
If a woman’s family has a history of birth abnormalities or is a member of a high-risk group, she should consult a genetic counselor to determine her baby’s risk.
It is critical to take prenatal vitamins and consume a balanced diet throughout pregnancy, in addition to taking the following precautions:
Avoid smoking and secondhand smoke; abstain from alcohol; abstain from all illicit drugs.
Obtain lots of exercise and rest; get prenatal care early and regularly.
Women can help lower their babies’ chance of birth problems by following certain pregnancy measures.
Summary
Childbirth refers to the act of giving birth to a child. It covers both labor and delivery. Generally, everything goes smoothly, although complications do occur. They may pose a danger to the mother, the infant, or both. Several of the most prevalent delivery complications include the following:
- Preterm (premature) labor occurs when labor begins before the completion of 37 weeks of pregnancy.
- Premature rupture of membranes (PROM), a condition in which your water breaks prematurely. If labor does not begin shortly afterward, the risk of infection increases.
- Labor that is not progressing, i.e., labor that has stalled. This may occur when
- Your contractions get softer.
- Your cervix does not dilate (open) sufficiently or dilates too slowly.
- The infant is incorrect.
- The baby is too large, or your pelvis is too tiny to pass through the delivery canal.
- The baby’s heart rate is abnormal. Frequently, an abnormal heart rate is not a cause for concern. However, if the heart rate becomes extremely rapid or extremely slow, it may indicate that your baby is not receiving enough oxygen or other issues.
Other Complication
- Umbilical cord complications, such as the cord becoming tangled around the baby’s arm, leg, or neck. Additionally, there is an issue if the chord emerges before the infant.
- Obstacles to the baby’s position, such as breech, in which the infant will emerge feet first
- Shoulder dystocia occurs when the baby’s head emerges, but the shoulder remains immobile.
- Perinatal asphyxia occurs when the infant does not receive enough oxygen in the uterus during labor or delivery or immediately after birth.
- Tears in the perineum, ripping of the vagina and adjacent tissues.
- Excessive bleeding, which can occur when the delivery breaks the uterus or if the placenta is unable to be delivered after the baby is born
- When a pregnancy lasts longer than 42 weeks, it is a post-term pregnancy.
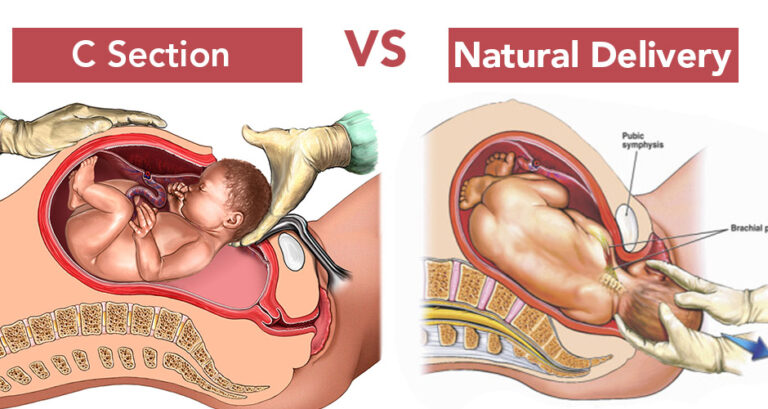
If you experience complications during childbirth, your health care practitioner may need to administer medications to stimulate or accelerate labor, utilize instruments to assist the baby’s exit from the birth canal or perform a Cesarean section.