Abscess: Evaluation For Skin Disease
Author: Alvin
Alvin
Category: Health

What is the definition of a skin abscess?
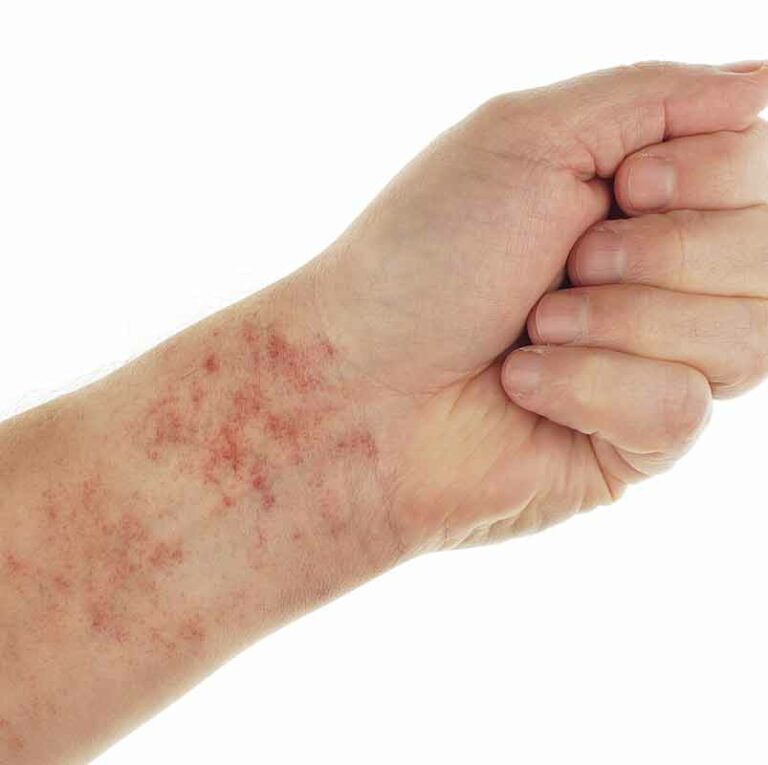
A skin abscess, alternatively referred to as a boil, is a lump that develops beneath or within the skin’s surface. Typically, this lump fills with pus or transparent fluid. A bacterial infection frequently causes it.
A skin abscess can manifest itself in any area of the body. On the other hand, abscesses most frequently occur on the back, face, chest, or buttocks. Skin abscesses can also develop in hair-bearing areas such as the underarms or groin.
The majority of skin abscesses are harmless and will resolve on their own. OTC lotions and drugs may be sufficient to aid in the healing process of a mild. Skin abscesses can occasionally be more difficult to treat and may require laceration or drainage.
In some situations, if left untreated, it can develop serious, perhaps life- threatening problems.
The most frequent causes of a skin abscess
Bacteria
Staphylococcus aureus is the most often encountered bacterium that causes skin abscesses. A skin abscess can develop due to a bacterial infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus bacteria entering the body through a hair follicle or a punctured or broken skin lesion.
If you have any of the following, you are at a greater risk of contracting this bacterial infection:
- intimate contact with someone infected with staph, which is why these illnesses are more prevalent in hospitals.
- a chronic skin condition, such as acne or eczema
- diabetes
- a compromised immune system, which can be brought by illnesses such as HIV
- a lack of hygiene
Hair follicles infected
Infected hair follicles, or folliculitis, can result in the formation of abscesses within the follicle. Follicles can become contaminated if the hair within the follicle becomes caught and unable to break through the skin, occurring following shaving.
Ingrown hairs refer to as trapped hair follicles. Ingrown hairs can act as a gateway to infection. Abscesses on or within a hair follicle frequently contain this type of ingrown hair.
Recognize a skin abscess
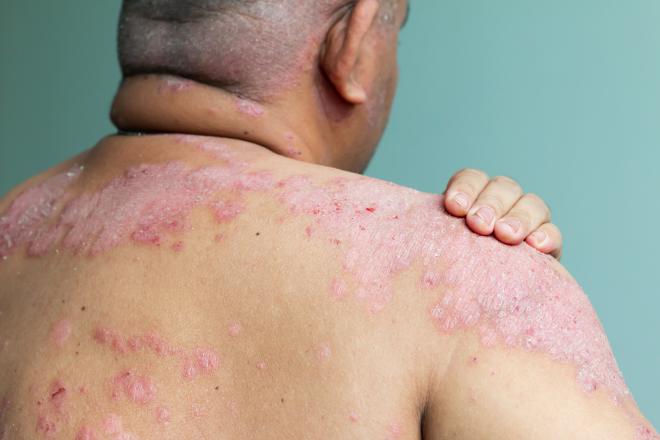
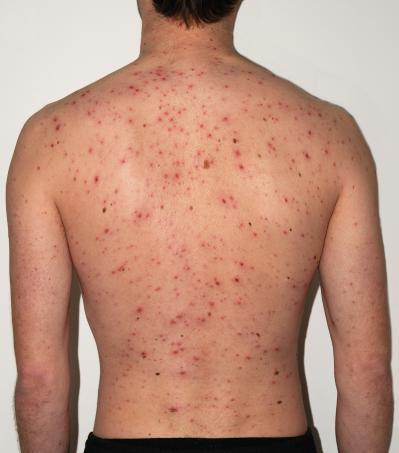
An abscess frequently presents as a pimple-like lump on the skin. It can, however, develop in size and resemble a cyst filled with fluid over time. Other symptoms may also be present, depending on the origin of the abscess. These symptoms may include the following:
- fever
- nausea
- chills
- swelling
- skin lesions
- Drainage of fluid
Additionally, the area surrounding the abscess may be uncomfortable and heated to the touch.
Recognize an abscess
A single tiny boil is rarely a reason for alarm. Often, you can treat it at home. However, if you have a boil and any of the following symptoms apply to you, contact your doctor immediately:
- A small child.
- You have reached the age of 65.
- Have a compromised immune system.
- You have undergone organ transplantation.
- You are undergoing chemotherapy or have recently completed chemotherapy.
- Located on your face or spine. If the abscess not treated, it may spread to your brain or spinal cord.
- You have a huge that has not healed after two weeks, and you also have a fever.
- It appears as though the abscess is expanding to other areas of your body.
- Becomes increasingly painful or throbbing.
- Your skin is puffy or highly red around.
- Your doctor will evaluate your medical history and conduct a physical examination to inspect the abscess visually. A thorough physical examination enables your doctor to determine whether the abscess results from an accident or ingrown hair.
Additionally, your doctor may collect a culture or a little amount of fluid from the abscess to check for germs. No more testing is required to diagnose an abscess.
However, if you have had recurrent skin abscesses and your doctor suspects an underlying medical condition, they may request a blood or urine sample.
 anukool/Getty Images
anukool/Getty Images
Facilitated by the Rubicon Project
Consequences of a skin abscess
In some situations, an abscess might develop into a dangerous infection. These may include the following:
- the infection’s progression, maybe to the brain or spinal cord
- sepsis, or blood poisoning
- Endocarditis is an infection of the heart’s inner lining.
- the formation of new abscesses
- tissue necrosis in the location, such as gangrene
- osteomyelitis, a severe bone infection
Methicillin-resistant Another possible consequence is methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). MRSA is a drug-resistant form of the bacteria responsible for most skin abscesses. While there are other medicines available to treat this strain, they are not always effective.
Abscess symptoms
A skin abscess frequently presents as a bloated, pus-filled bump beneath the skin’s surface. Additionally, you may experience additional infection-related symptoms, such as fever and chills.
Although identifying inside the body is more challenging, indications include the following:
- discomfort in the afflicted area
- a scorching temperature
- generally unwell
When to consult your physician
Consult your physician if you suspect you may have an abscess. They can inspect a cutaneous abscess or refer you to the hospital if an internal abscess is suspected.
Abscesses have a variety of causes.
The majority of abscesses are the result of a bacterial infection.
When germs enter the body, the immune system mobilizes infection-fighting white blood cells to the site of infection.
As the white blood cells assault the germs, some surrounding tissue dies, forming a hole filling with pus and forming an abscess. The pus is composed of decomposing tissue, white blood cells, and bacteria.
Internal abscesses frequently occur due to another illness, such as an infection elsewhere in the body. For instance, if your appendix ruptures due to appendicitis, germs can spread throughout your tummy (abdomen) and result in the formation.
How to treat an abscess
A minor cutaneous abscess may drain spontaneously or may just diminish, dry up, and resolve without treatment.
However, larger abscesses may require antibiotic treatment to eradicate the infection and drainage of the pus. Put a needle through your skin or create a small incision in the skin directly above.
How to avoid a skin abscess
Maintaining clean, healthy, and mainly bacteria-free skin can help lower the chance of getting skin abscesses.
You can limit the danger of bacteria spreading by doing the following steps:
- Regularly wash your hands.
- encouraging members in your household to regularly wash their hands
- utilizing separate towels and refraining from sharing baths
- reserving any common equipment, such as gym equipment, saunas, or swimming pools, until your skin is completely treated and healed
- Avoid manually extracting pus from the abscess since this can easily transfer the bacteria to other areas of your skin. If you use tissues to remove pus from your abscess, discard them immediately to prevent germs from spreading. After disposing of the tissues, wash your hands.
Avoid nicking your skin when shaving your face, legs, underarms, or bikini area. Avoid sharing razors and toothbrushes.
Additionally, it may help minimize your risk of developing skin abscesses by:
- consuming a nutritious, balanced diet
- if you are overweight or obese, you must lose weight.
- smoking cessation
- Internal abscesses are difficult to prevent because they are frequently consequences of other illnesses.
Additional forms of abscess
Numerous more forms of abscesses are not described in detail here, including the following:
- an anorectal abscess a collection of pus in the lower abdomen (the rectum and anus)
- a brain abscess - a somewhat uncommon but potentially fatal buildup of fluid inside the skull
- a dental abscess a collection of pus beneath a tooth or in the gums and bone that support it
- Quinsy (peritonsillar abscess) is a pus-filled space between the tonsils and the throat wall.
- a pilonidal abscess a collection of pus in the skin of the buttocks aperture (where the buttocks separate)
- an abscess of the spinal cord a collection of pus surrounding the spinal cord