HYPOGLYCEMIA: Types, Symptoms, Causes
Author: Shiela Lupiba
Shiela Lupiba
Category: neutrinos
Tags: health, blood, hypoglycemia, sugar, neutrinos

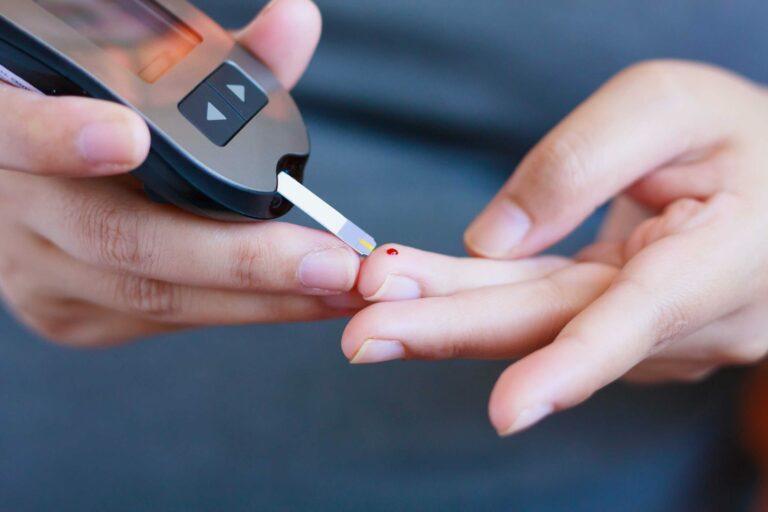
Hypoglycemia occurs when your blood sugar (glucose) level is lower than normal (below 70 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter). Glucose is the primary source of energy in your body.
People get confused between hypoglycemia and diabetes. Hypoglycemia is when the body produces too much insulin while Diabetes is a medical condition where the body cells do not produce enough insulin.
TYPES OF HYPOGLYCEMIA
- Reactive -it is the general term for having a hypoglycemia after eating, which is when blood glucose levels become dangerously low following a meal.
- Non-diabetic -it is a rare condition characterized by low blood glucose levels in people who do not have diabetes.
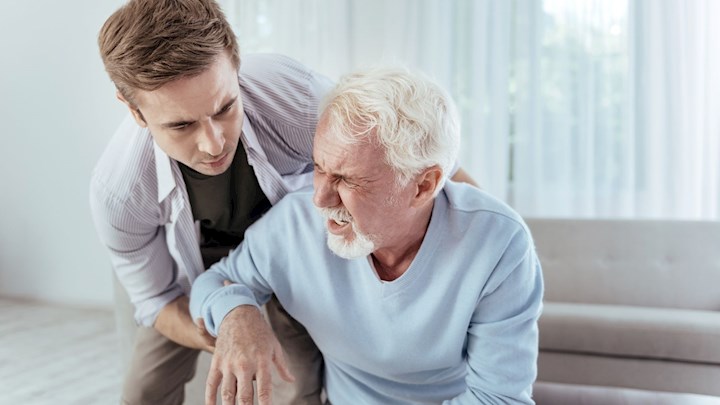
SYMPTOMS
Most people feel symptoms of hypoglycemia when their blood sugar is 70 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or lower. The symptoms may be different, depending on how low your blood sugar goes. They usually include:
- Blurred vision or changes in vision

Low blood sugar can also lead to double vision and blurred vision. While high blood sugar can alter the shape of your eye’s lens, low blood sugar does not, and this eyesight problem can be resolved sooner if your blood sugar is restored after a meal or snack.
2. Neurological issues

Hypoglycemia reduces the glucose supply to the brain, causing dizziness, fatigue, weakness, headaches , inability to concentrate, and confusion.
3. Fast or pounding heartbeat

If you have low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), foods high in processed sugars and carbohydrates can trigger heart palpitations.
4. Nausea or hunger

When people have mild low blood sugar, whether they have diabetes or not, they may feel extremely hungry and often nauseated. Also, the release of the stress hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, causes this symptom combination, which is the first sign of low blood sugar.
CAUSES
- Medications Taking someone else’s oral diabetes medication accidentally is a possible cause of low blood sugar.
- Too much alcohol. Heavy drinking without eating can prevent your liver from releasing stored glucose into your bloodstream, resulting in hypoglycemia.
- Adrenal or pituitary gland disorders. These organs (pituitary or adrenal) affect the hormones that control the glucose production.
- Not eating enough. Blood sugar drops when a person do not eat much carbohydrates.
- Postponing or skipping a meal. Skipping meals can be dangerous because it can cause low blood sugar.
TREATMENT
- Eat or drink 15 to 20 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates
- Recheck blood sugar levels 15 minutes after treatment
- Have a snack or meal
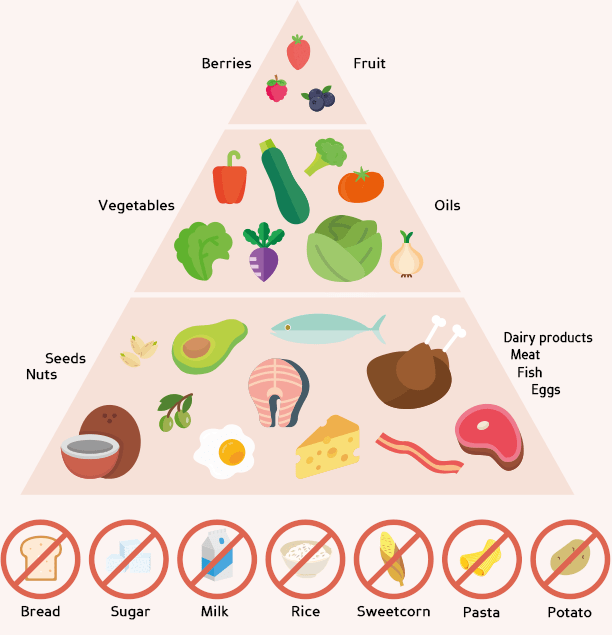
FOODS TO AVOID AND EAT
If you have symptoms of hypoglycemia, it's important to monitor the glycemic index (GI) of the foods you eat and alter your diet if necessary. Moreover, keep reading to learn more about the hypoglycemia diet and foods to eat and avoid to keep your symptoms in check. Here is the list of the food that you need to avoid and eat:
-
FOODS TO AVOID
-
Processed foods
- Fried foods
- MSG (monosodium glutamate)
- All soft drinks
-
Hot dogs, sausages, and deli meats
-
FOODS TO EAT
-
Lean Meats
- High-quality protein (fish, poultry, lean meat, free-range eggs)
- Fresh fruits. Eat blueberries and raspberries often;
- Leafy vegetables
- Raw, unsalted, unseasoned nuts and seeds
- Filtered water
Consequently, hypoglycemia is common in people with diabetes. It can cause serious health problems if not treated. You can avoid hypoglycemic episodes by monitoring your blood sugar.