Goiter: What to Do If You Have It
Author: Alvin
Alvin
Category: Women's Health
Tags: health, goiter, women's health, gland, thyroid
Goiter is a disorder in which the thyroid gland enlarges and becomes more visible. Located in the neck behind the Adam’s apple. The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland that produces thyroid hormone.
A goiter (pronounced “GOI-tur”) is an abnormal growth of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland that is located near the base of the neck. Directly below the Adam’s apple. It produces thyroid hormone.
This goiter can be defined as an overall enlargement of the thyroid gland. Or it can be caused by abnormal cell proliferation that results. In the formation of one or more lumps (nodules) in the thyroid gland. A goiter may be linked with no change in thyroid function. Or it may be associated with an increase or reduction in thyroid hormone production.
The most common cause of goiters throughout the world is a deficiency of iodine in the diet. When it comes to goiters in the United States, where the use of iodized salt is popular. They are produced by disorders that alter thyroid function. Or by factors that interfere with thyroid growth.
Treatment for goiter is dependent on the source of the goiter, the symptoms. And any complications that may arise as a result of the goiter. Small goiters that aren’t obvious and don’t cause difficulties. Are usually not necessary to cure or remove.
The thyroid gland is responsible for the production of the hormones thyroxine (commonly known as T4). And triiodothyronine (also called T3). (Outside of the thyroid, the majority of the T4 is converted to T3.) Body temperature, mood, and excitability, pulse rate. Plus digestion are just a few of the bodily systems that these hormones influence.
Symptoms
Except for a swelling at the base of the neck. The majority of persons who have goiters show no indications or symptoms. In many circumstances, the goiter is so small. That it is only identified during a normal medical exam. Or during an imaging test for another medical problem.
The presence or absence of other indications or symptoms is dependent. On whether or not thyroid function is altered, how quickly the goiter grows. And whether or not it obstructs breathing.
The most common sign of a goiter is a swelling in the neck W.hich can be treated with medication. It is possible that the swelling will be significant enough to be felt with the hand.

The degree of swelling and the severity of symptoms caused by the goiter. Vary from person to person depending on their genetics.
When further symptoms appear, the following are the most frequently reported. Throat tightness, coughing, and hoarseness, difficulty swallowing. And, in severe cases, difficulties breathing (also known as dysphagia).
Because of the underlying etiology of the goiter, it is possible that other symptoms will manifest themselves.
Hyperthyroidism, also known as an overactive thyroid. Which can manifest itself in the form of symptoms. Such as anxiousness, palpitations, and excessive activity.
What Causes Goiter?
Iodine deficiency is one of the most common reasons of goiter formation. This used to be a common source of goiter in the US, but not anymore. The thyroid gland’s main job is to concentrate iodine from the blood to generate thyroid hormone. The thyroid gland cannot create enough thyroid hormone without iodine.
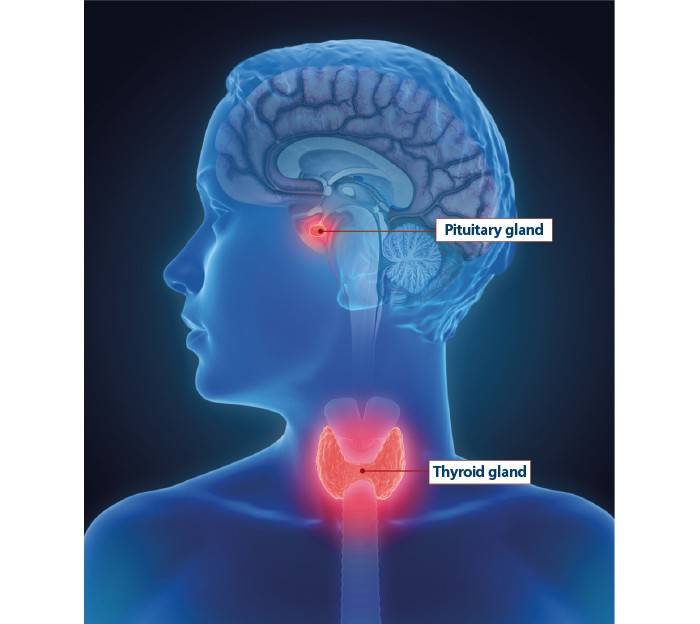
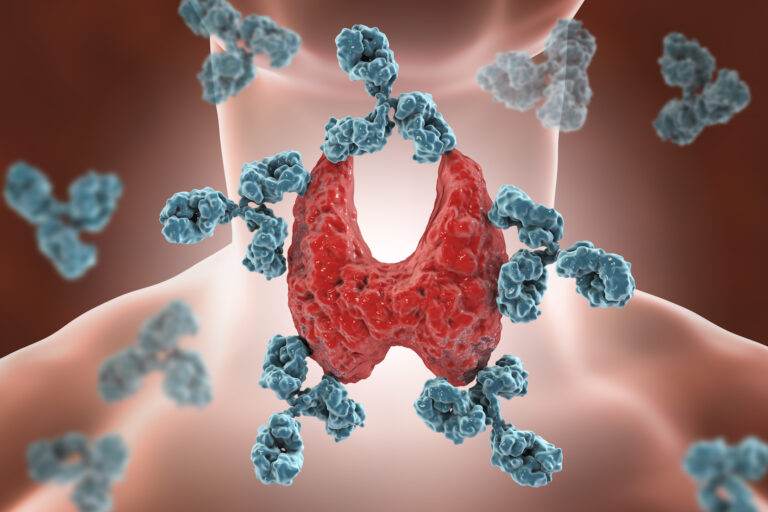
In the US, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is more common. This is an autoimmune disease where the immune system destroys the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland’s ability to produce thyroid hormone decreases with age. To activate the thyroid, the pituitary gland secretes more TSH. This stimulation induces thyroid growth, leading to goiter.
Graves’ illness is another cause of goiter. The immune system produces thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI) (TSI). Like TSH, TSI causes a goiter by enlarging the thyroid gland. But TSI also boosts thyroid hormone production (causes hyperthyroidism). Whereas, when the pituitary detects too much TSH, it ceases to secrete. Despite this, the thyroid gland grows and produces thyroid hormone. This causes a goiter and hyperthyroidism.
Multinodular goiters are also prevalent. Thyroid nodules induce thyroid enlargement in people with this condition. A nodular feeling gland is typically found on physical exam. When first diagnosed, patients may have a single large or several smaller nodules in the gland (see Thyroid Nodule brochure). The thyroid may not be enlarged in the early stages of a multinodular goite. With many tiny nodules. Unlike the other goiters addressed, the cause of this one is unknown.
There are numerous less common causes of goiter besides the main ones. Some are inherited, some are caused by thyroid injuries or infections. And some are tumors (both cancerous and benign tumors).
Types of Goiters
Because a variety of factors can cause your thyroid to grow. There are many different forms of goiters. Here are a few examples:
Simple Goiters

Simple goiters, which occur when your thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones. These are the most common. In order to compensate for this, the thyroid expands in size.
The thyroid gland develops simple goiters when it is unable to produce enough hormones. To meet the needs of the body. Because of this deficiency, the thyroid gland attempts to compensate by increasing in size.
Endemic Goiters
These goiters, which are also known as colloid goiters, are caused by a lack of iodine in your diet. Your thyroid produces hormones with the help of iodine. People who live in nations where iodine is added to table salt. Such as the United States, are less likely to get this type of goiter.
The condition known as endemic goiter affects people who live in particular parts of the world. Where they do not consume enough iodine (iodine is necessary to make thyroid hormone). For example, in some parts of central Asia. And central Africa, a lack of iodine in the diet is still a widespread problem. The fact that iodine is added to table salt in the United States. Also the other nations means that this type of goiter is less common in these areas.
Sporadic Goiters
Goiters that are sporadic or harmless in nature, with no recognized etiology in most cases. They can be triggered by certain medications and medical conditions.
In the majority of cases, there is no recognized cause for sporadic goiters. Certain medications have linked to this form of goiter in some situations. This sort of goiter, for example, can caused by the chemical lithium. Which used to treat some mental health disorders as well as other medical conditions.
Goiter Treatment
It is possible that a goiter will not require treatment. Especially if it is tiny and thyroid hormone levels are within normal range. However, if your thyroid hormone levels are very high or excessively low, you will require medication.
The goal of treatment is to restore the thyroid hormone levels to their normal range. Depending on the source of your goiter and the severity of the condition. Your doctor may recommend one of the following treatments:
Medication

Depending on the severity of your hypothyroidism. Your doctor may prescribe a thyroid hormone replacement therapy. When the medication begins to work. It is possible that the thyroid will begin to shrink back to its usual size. A huge nodular goiter with a significant amount of internal scar tissue. On the other hand, will not diminish with treatment. Goiters induced by inflammation may treated with aspirin or corticosteroids, among other medications.
Surgery
Because of the discomfort associated with a goiter. If the goiter causes excessive thyroid hormone production that is unresponsive to medication. Whereas if goiter is large enough that it causes symptoms as a result of its size. Or if the goiter becomes cancerous, the thyroid gland may have to surgically removed. Alternatively, they may only remove a portion of it. Afterwards, you may be need to take thyroid hormone medication for the rest of your life. If your condition worsens.
Iodine that is radioactive
This is a medication that you use to treat an overactive thyroid. It causes thyroid cells to die, causing the thyroid to shrink. Following this procedure, you will almost certainly require the use of hormone medications for the rest of your life.
If you have a goiter, your doctor may want to check on it on a regular basis. With ultrasound to make sure it isn’t growing larger. Or developing suspicious-looking nodules that might necessitate a fine-needle biopsy. If you have a goiter, your doctor may want to check on it on a regular basis. With ultrasound to make sure it isn’t growing larger. As well as developing suspicious-looking nodules that might necessitate a fine-need