G6PD Deficiency
Author: Shiela Lupiba
Shiela Lupiba
Category: Child's Health
Tags: health, men's health, g6pd, blood, deficiency, child's health
What is G6PD?
G6PD deficiency is a disease that is passed down via families. This condition arises when the body does not have sufficient amounts of an enzyme known as G6PD (glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase). The healthy functioning of red blood cells contributes to by this enzyme. Anemia that is hemolytic can be caused by a deficiency in this enzyme. When this occurs, the red blood cells are destroyed at a rate that is greater than their production.
G6PD is also accountable for maintaining the health of red blood cells so that these cells can continue to function normally and have a typical lifespan. When there is not enough of it, it causes early breakdown of red blood cells. This premature loss of red blood cells refers to as hemolysis, and it can ultimately lead to the condition known as hemolytic anemia.
Hemolytic anemia characterizes by a decrease in the amount of oxygen that delivers to the body’s organs and tissues as a consequence of the destruction of red blood cells at a rate that exceeds the capacity of the body to replace them. This can lead to symptoms including shortness of breath, yellowing of the skin and eyes, and weariness.
Symptoms
The following are examples of possible symptoms of a G6PD deficiency:
-
High blood bilirubin levels cause dark, yellow-orange urine.
-
Dyspnea occurs when the rapid breakdown of red blood cells depletes the body’s oxygen supply.
- Paleness causes by a patient’s low red blood cell count. Symptoms of g6pd
- Fatigue – Diet, exercise, and sleep can help. The tired person must rest to re-energize.
-
Rapid heart rate can be avoid by avoiding g6pd deficiency-triggering meals. Eat heart-healthy foods.
spleen enlargement occurs when it filters blood cells for hemolytic anemia. -
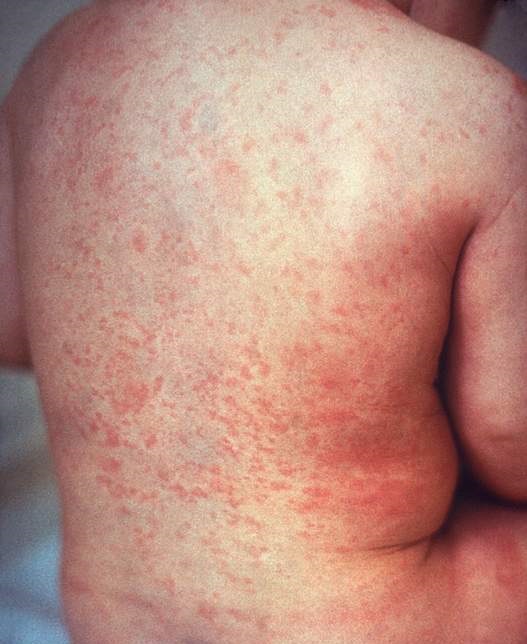
Jaundice – skin and mucous membranes, especially the whites of the eye (sclerae), turn yellow; bilirubin is a substance left in the blood after a red blood cell destroy; the liver excretes it. When red blood cells destroys too quickly, the liver can’t keep up with the bilirubin in the blood, causing yellow skin.
- rapid rise in body temperature – Fever is a sign that the body is battling anything foreign, like the meal or drug that caused g6pd symptoms.
-
general weakness – If the patient is overtired, he will feel his physical condition worsening.
-
 Jaundice is one of the symptoms of G6PD Deficiency
Jaundice is one of the symptoms of G6PD Deficiency
It is extremely important for the patient, as well as his family and friends, to be aware of the foods that can be hazardous to him in order to aid in the prevention of these symptoms of g6pd deficiency. The patient will be able to have a normal and healthy life if they stay away from the foods and drugs that are hazardous to them. This will also make the patient more comfortable. It is essential to effectively communicate with the patient in order to ensure that they are consuming only those foods that are permitted.
Causes
G6PD deficiency is a genetic disorder that can be inherit from either one or both of a person’s parents by the child. The faulty gene that is responsible for this impairment locate on the X chromosome, which is one of the two chromosomes that are found in humans. In contrast to women, men only have one copy of the X chromosome. Women, on the other hand, have two copies. G6PD insufficiency can be cause by a single mutated copy of the gene in males. This is sufficient to create the condition.
In most circumstances, a mutation in both copies of the G6PD gene requires for a female affects by the condition. However, there are instances in which a single copy of the gene can be mutate and still cause symptoms in a female. Because females have two copies of the X chromosome. Males are significantly more likely to impact by G6PD deficiency than females are.
Diagnosis
A straightforward blood test is all that’s require to establish a G6PD deficiency diagnosis with your doctor. It’s possible that you’ll require this test if:
- Your ancestors hail from a region in which this condition is quite prevalent.
- You and/or members of your family have a history of G6PD deficiency.
- You have a sort of anemia that we cannot identify.
In order to arrive at an accurate diagnosis, your healthcare professional may do additional testing.
Why do more men have G6PD deficiency?
G6PD deficiency is an X-linked recessive disease that is passed down through families. What that entails is as follows:
- Because males only have one copy of the X chromosome, there is a greater chance that they will pass on a mutant G6PD gene to their offspring. This makes G6PD deficiency more prevalent in males.
- However, females have two copies of the X chromosome. Which improves the likelihood that they will pass on a normal G6PD gene rather than a mutant G6PD gene to their offspring.
- The vast majority of females can inherit the mutant gene without actually suffering from G6PD deficiency. If either copy of the G6PD gene mutates, it is possible that some females will impact by the condition. It’s possible that females who carry just one mutant gene will have reduced G6PD activity and a lower probability of acquiring symptoms.
Treatment
The vast majority of patients do not require any form of treatment since they are able to control their illness by avoiding the triggers. Your physician will provide you with a list of things to stay away from as well as advice on how to treat the disease.
In the event that you acquire anemia, you will require treatment for it, which may involve receiving a blood transfusion. Babies who have jaundice are given a treatment that involves placing them under specialized lights referred to as “bili lights.” In the most extreme circumstances. It may be necessary to perform an exchange transfusion. In which some of the infant’s blood is taken and then replaced with blood or plasma from a donor.
Always be sure to inform your doctor about your illness before beginning any treatment with medication. This will ensure that they do not prescribe anything that could potentially bring on your disease. If you buy medicine without a prescription, you should consult your local pharmacy and pay close attention to the product label. You must also use extreme caution while utilizing any complementary or alternative therapies.
Those who lack G6PD are more likely to have haemolysis if they contract a virus or another ailment that puts their bodies under stress. If either you or your child develops an infection, you should visit a physician.