Brain Tumor: Symptoms and Its Treatment
Author: Alvin
Alvin
Category: Health

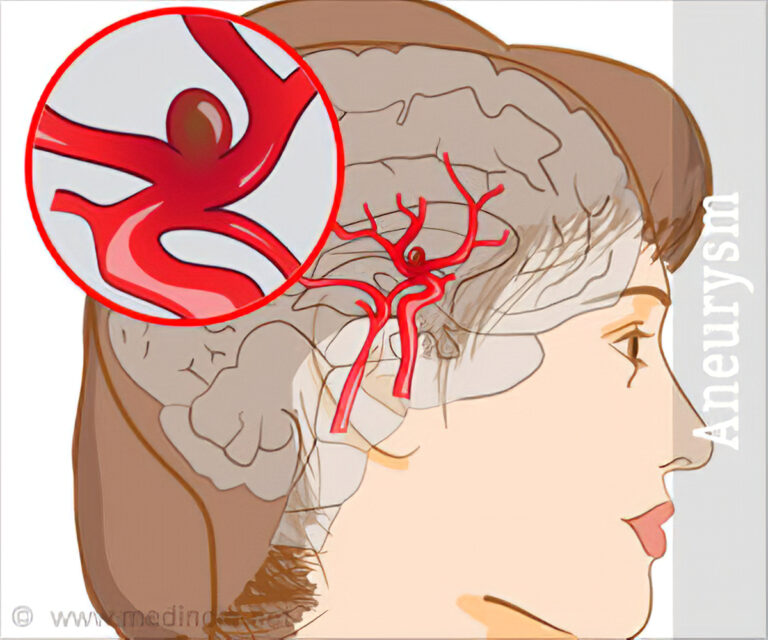
A brain tumor is a mass of abnormal cells located in your brain. The bone structure of your skull serves to protect your brain within. The robust growth of anything within a confined space might become an issue. Tumors of the brain can be either malignant (cancerous) or noncancerous (benign). Benign or malignant tumors might cause the increased pressure inside your skull. Pregnant women and children are more at risk since it causes brain damage and is life-threatening.
When cancer cells migrate to your brain from another organ, such as your lung or breast, a secondary brain tumor, also known as a metastatic brain tumor, will develop.
What are the symptoms of a brain tumor?
Patients who suffer from brain tumors have varying symptoms depending on where and how giant the tumor is. Directly damaging tumors are the ones that invade brain tissue, and pressure on the surrounding brain tissue is due to tumors. As the tumor grows, you will be feeling the tension in your brain tissue.
Tumors in the brain are also a prevalent cause of headaches. occur quite frequently;
- get worse while you are asleep
- vomiting
- eyesight which has blurred or double vision
- foggy mind attacks (especially in adults)
- a lack of coordination
Another commonly occurring symptom is:
- clumsiness
- episodic memory loss
- confusion
- Hearing, tasting, and smelling difficulties can indicate changes in the capacity to write or read.
- loss of consciousness and sleepiness, which may involve unconsciousness
- dizziness or vertigo as a result of difficulties swallowing
- include any eye conditions, such as eyelid droop, and uneven pupil size
- out of control
- tremors of the hand
- the loss of one’s balance
- uncontrollable defecation and constipation
- difficulties speaking or understanding what others are saying
How are brain tumors diagnosed?
To correctly diagnose a brain tumor, a physical exam and a review of your medical history are required.
The neurological evaluation comprises a highly in-depth physical assessment. To ensure that your cranial nerves are still working, your doctor will carry out a test. This is where the nerve stems in your brain originate.
An ophthalmoscope, medical equipment that shines a light into your pupils and onto your retinas, is used to examine your eyes. This serves as a mechanism to enable your doctor to explore how your pupils react to light. Also, this technique allows your doctor to examine your eyes directly to detect if the optic nerve swollen. Changes in the optic nerve can occur when pressure increases inside the skull.
Brain Tumor Treatment
the particular type of tumor, as well as its location in the brain
- tumor types
- The tumor’s size
- the tumor’s location
- your overall physical well-being
Approximately 90% of all malignant brain tumors treat with surgery. The aim is to minimize damage to the healthy areas of the brain while removing as much of the cancer as feasible. It is easier to get certain types of tumors out of the way, as they tend position in an accessible location. However, certain types of tumors may be located in an area that limits how much of the tumor may be removed. Removing even part of the brain cancer can be of benefit.
For brain surgery, there are many risks, including infection and hemorrhage. Neutropenic (benign) tumors, which consider being clinically threatening, may also eliminate. The rules for the type of primary cancer apply to metastatic brain tumors.
A combination of treatments, including radiation therapy and chemotherapy, can be used in conjunction with surgery.
Recovery from a neurosurgical procedure aids by physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy.
What is the prevalence of brain tumors?
Each year, approximately 85,000 people in the United States are diagnosed with brain tumors. Around 60,000 of those tumors are benign, while approximately 25,000 are malignant.
Who are the victims of brain tumors?
Men are more likely than women to develop brain tumors. While they are more prevalent in older adults, they can occur at any age. Brain tumors are the most common type of cancer in children under the age of 14.
What types of brain tumors are there?
Doctors classify brain and central nervous system tumors according to their location and the type of cells involved.
Brain tumors that are typically benign include the following:
Acoustic neuroma: These benign tumors develop on the vestibular nerve (the nerve that leads from the inner ear to the brain). Additionally, acoustic neuromas refers to as vestibular schwannomas.
Gangliocytoma: These tumors of the central nervous system develop in neurons (nerve cells).
Meningioma: This is the most frequently occurring type of primary brain tumor. Meningiomas are slow-growing tumors. They develop in the meninges, the tissue layers that surround the brain and spinal cord. Meningioma can be malignant in extremely rare cases.
Pineocytoma: These benign tumors develop in the pineal gland, which is located deep in the brain and produces melatonin hormone.
Pituitary adenoma: These tumors develop in the pituitary gland at the base of the brain. The pituitary gland is responsible for producing and regulating hormones in the body. Adenomas of the pituitary are typically very small.
Chordoma: Typically, these slow-growing tumors begin at the base of the skull or the base of the spine. They are mostly harmless (not cancerous).
Cancerous brain tumors include the following :
Glioma: These tumors form in the glial cells that surround and support nerve cells. Gliomas account for two-thirds of all cancerous primary brain tumors. Gliomas classify into the following categories:
Astrocytoma: Astrocytomas are benign tumors that develop in glial cells called astrocytes.
Glioblastoma: Glioblastomas are aggressive astrocytomas that grow rapidly.
Oligodendroglioma: These rare tumors develop in the cells that produce myelin (a layer of insulation around nerves in the brain).
Medulloblastoma: Medulloblastomas are a type of tumor that grows rapidly and forms at the base of the skull. These are the most frequently occurring malignant brain tumors in children.
What factors contribute to the development of a brain tumor?
Doctors are unsure of the cause of the majority of brain tumors. Mutations (differences) or defects in genes can cause the uncontrollable growth of brain cells, resulting in a tumor.
The only known environmental risk factor for brain tumors is excessive radiation exposure from X-rays or previous cancer treatment. Certain types of brain tumors occur as a result of hereditary conditions passes down through family members.
What symptoms indicate the presence of a brain tumor?
Certain individuals with brain or central nervous system tumors exhibit no symptoms. In some instances, doctors discovered a tumor while treating another condition.
A brain tumor may cause symptoms as it grows and presses on nearby nerves or blood vessels. They may include the following:
Continuous or severe headaches, or headaches that occur in the morning or subside after vomiting.
- Changes in behavior or personality.
- Confusion.
- Balance or coordination problems.
- Concentration difficulties.
- Vomiting and nausea.
- Numbness, weakness, or tingling in a particular area, side, or face.
- Hearing, vision, or speech difficulties.
- Seizures.
- Unusual slumber.
- Memory, thinking, speaking, and understanding language difficulties.
How can a brain tumor be prevented?
A brain tumor cannot be prevented. Avoiding environmental hazards such as smoking and excessive radiation exposure can help reduce your risk of developing a brain tumor.
What are groups of people at risk of developing a brain tumor?
Individuals who are at an increased risk of developing brain tumors include those who have:
Cancer runs in the family.
A mutation in the DNA that results in abnormal cell growth.
Prolonged exposure to radiation from X-rays or other cancer treatments.
Exposition to specific chemicals (possible cause).