Brain Diseases: Risk Factor to Health
Author: Alvin
Alvin
Category: Mental Health

What is brain diseases?
Brain diseases are due to a mixture of genetic, environmental, and accidental factors, which may affect the brain at the molecular and cellular.
Your brain serves as the control center for your body. It is a component of the nervous system, the spinal cord and a complex network of nerves and neurons. The nervous system, as a whole, regulates everything in your body, from your senses to your muscles.
When the brain is injured, it can influence various functions, including memory, sensation, and even personality. Any ailment or disability that affects your brain is considered a brain disorder. This category includes conditions induced by the following:
- Illness
- genetics
- traumatic injury
This is an extensive range of illnesses with widely disparate symptoms and degrees of severity. Continue reading to learn about several of the most common types of brain illnesses.
What are the various sorts of mental disorders?
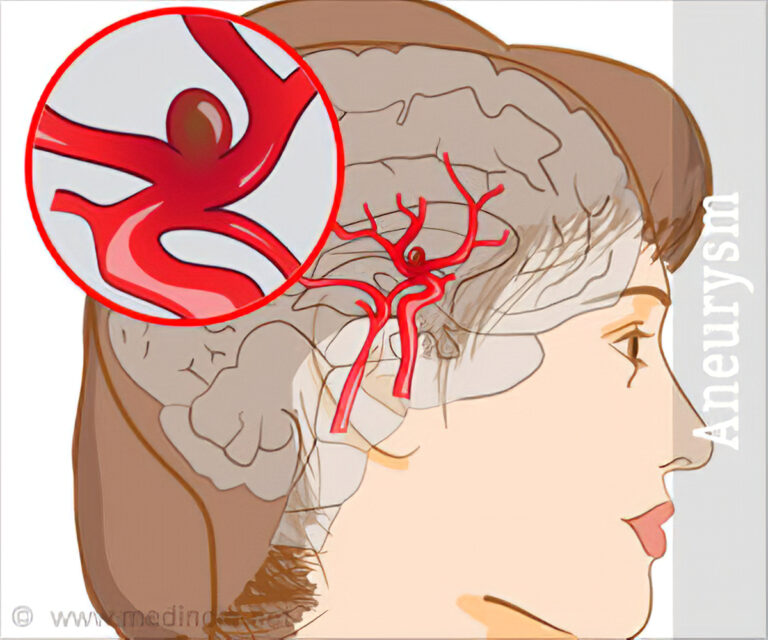
Injuries to the brain
Brain injuries are frequently the result of forceful trauma. Trauma can cause damage to the brain, neurons, and nerves. This impairment impairs the ability of your brain to communicate with the rest of your body. Several types of brain injuries include the following:
- hematomas
- clots of blood
- brain contusions or bruises
- cerebral edema, or internal swelling of the skull
- concussions
- strokes
Among the symptoms of brain damage are the following:
- vomiting
- nausea
- problem with speech
- ear bleeding
- numbness
- paralysis
- memory impairment
- difficulties with concentrating
- Hearing, speech, or vision changes.
- Partial or total paralysis.
- Seizures
- Instability or dizziness.
- Headaches.
- Vomiting and nausea.
- There are tremors and shakes.
- Arms or legs are weak.
- Suffering from a loss of scent or taste.
- Excessive exhaustion.
- Reading or writing difficulties, even though the individual was previously able to do so.
- Inexplicable pain.
- Breathing difficulties.
- Walking difficulty.
- Issues with swallowing.
- Speech alters.
You may later develop:
- hypertension
- a reduced heart rate
- dilatation of the pupils
- breathing irregularly
Treatment options may include medication, rehabilitation, or brain surgery, depending on the nature of the injury.
Approximately half of individuals who have serious brain injuries require surgery to remove or repair damaged tissue or to relieve pressure. Individuals who have small brain injuries may require little treatment beyond pain medication.
Numerous individuals who have sustained brain injuries require rehabilitation. This may involve the following:
- bodily treatment
- treatment for speech and language
- psychiatry
Tumors of the brain
Tumors can occur in the brain and can be quite deadly. These are primary brain tumors. In some situations, cancer that begins elsewhere in the body travels to the brain. These refers to as secondary brain tumors or metastatic brain tumors.
Brain tumors can be malignant (cancerous) or benign (noncancerous) (noncancerous). Doctors classify brain tumors into grades 1, 2, 3, or 4. Increased numbers suggest more aggressive cancers.
Diseases of the nervous system
Neurodegenerative diseases gradually degrade the brain and nerves. They can alter your personality and create uncertainty. Additionally, they can cause damage to the brain’s tissue and nerves.
Certain brain illnesses, such as Alzheimer’s, may develop with age. They have the potential to affect your memory gradually and thought processes.
Because neurodegenerative disorders are irreversible, symptoms typically worsen as the disease develops. Additionally, new signs are likely to develop over time.
While there is currently no cure for neurodegenerative illnesses, treatment can still be beneficial. Treatment for these disorders focuses on symptom reduction and maintaining a high quality of life. Treatment frequently includes the administration of drugs to alleviate symptoms.
Mental illnesses
Is a broad and diverse set of ailments that impair your ability to behave normally.
Mental diseases present with a variety of symptoms. Individuals can have vastly different experiences with the same mental diseases. If you observe a change in your behavior, mental patterns, or moods, you should consult your physician.
Medication and psychotherapy are the two primary modes of treatment for mental diseases. Different strategies are more effective in various circumstances. Numerous individuals discover that a blend of the two is most beneficial.
If you believe you may have a mental illness, it’s critical to speak with your doctor to develop a treatment plan that works for you. There are numerous resources accessible - avoid self-medicating.
What variables contribute to the chance of developing a brain disorder?
Anyone can get a brain condition. The risk factors for various forms of brain illnesses vary.
Traumatic brain damage is most prevalent in children under four, young adults aged 15 to 25, and adults aged 65 and beyond.
Brain tumors can strike individuals of any age. Your risk determine by your genetics and your exposure to risk factors in the environment, such as radiation.
The most significant risk factors for neurodegenerative disorders are advanced age and family history.
How are mental illnesses diagnosed?
A brain problem diagnosed by your primary care physician or a neurological specialist.
Your doctor will almost certainly conduct a neurological examination to evaluate your vision, Hearing, and balance. Additionally, your doctor may obtain pictures of your brain to aid in diagnosis. CT, MRI, and PET scans uses diagnostic imaging technologies.
Additionally, your doctor may need to examine fluid from your brain and spinal cord. This enables them to detect brain bleeding, infection, and other problems.
Generally, mental health illnesses are diagnosed based on your symptoms and background.
What is the outlook for the long term?
The prognosis for individuals with brain illnesses varies according to the type and degree of the disorder. Certain diseases can be addressed well with medicine and therapy. For instance, millions of people who suffer from mental problems have quite normal lives.
Other conditions, such as neurodegenerative diseases and certain types of traumatic brain traumas, are incurable. Individuals suffering from these illnesses frequently have irreversible changes in their behavior, mental talents, and coordination. In these instances, treatment will be directed toward assisting you in managing your illness and regaining as much independence as possible.
Causes
According to the NINDS, the following are known causes of brain disease:
-
Inflammation
-
Brain swelling causes by infection, an autoimmune reaction, or some other unknown factor. This can irritate and destroy brain tissue over time. Multiple sclerosis and vasculitis are two inflammatory diseases of the brain. A traumatic brain injury can result in inflammation and direct brain damage.
-
Stroke
-
Disrupted blood flow to the brain can result in the death of brain cells, impairing movement, speech, and thought.
Tumors of the Brain
Tumors can compress tissues and nerves, impairing cognitive function.
Genetics
Certain brain illnesses, such as Tay-Sachs, Huntington’s, muscular dystrophies, and Wilson disease, are inherited. Typically, identify through a clinical examination, family history, and, in rare situations, genetic testing.