Back Pain: Everything You Need to Know
Author: Alvin
Alvin
Category: Fitness
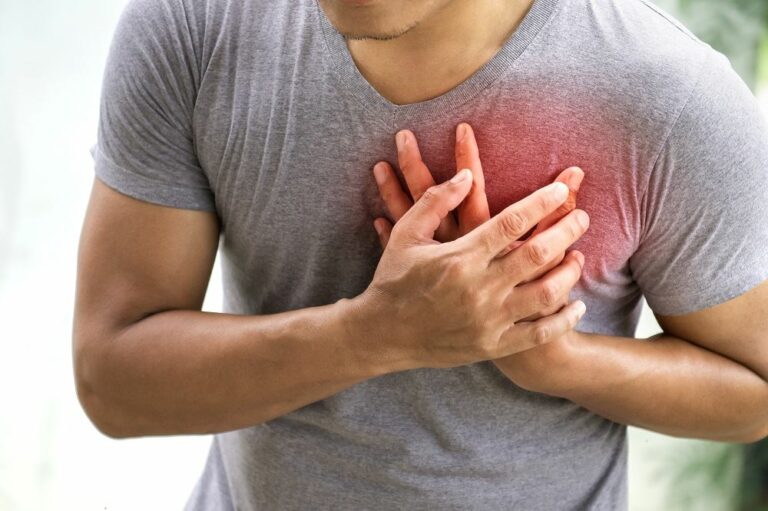
Back pain is one of the most commonly experienced causes of both medical and work-related absences.
Unfortunately, most back pain episodes can be prevented or relieved with good planning. If the treatment doesn’t work, simple home care and good body mechanics can often help you heal your back within a few weeks and keep it from returning to pain.

Symptoms
Backpain can have mild discomfort to unbearable agony. Also, the pain can sometimes extend from your knee down your leg, or increase when you bend, twist, lift, stand, or walk.
Causes
Injury to the muscle. Back muscles and spinal ligaments can be strained by heavy lifting or a sudden awkward movement. Muscle spasms caused by constant strain on the back are painful if you’re not in good physical condition.
Rupture Disks. Serve as shock absorbers between the vertebrae (spinal bones) in your spine. A soft material within a disk can press on a nerve irritating. Back pain is not always associated with a bulging or ruptured disk. Disk disease often appears incidentally when you have other spine X-rays as part of a different medical investigation.
Arthritis. In cases of osteoarthritis, the lower back can be affected. Spinal stenosis can sometimes be the result of arthritis in the spine.
Osteoporosis. A painful vertebral fracture can develop if your bones become brittle and porous.
Risk Factors
Back pain is a common ailment for everyone, even children and teenagers. Back pain risk factors may include:
Age. Back pain is more prevalent among adults over the age of 30 and up.
Not getting enough exercise. Muscles that are weak or unused may lead to lower back pain.
Being overweight. When you carry too much extra weight, it places a great deal of strain on your back.
Diseases. A variety of illnesses, including arthritis and cancer, can cause back pain.
Unhygienic lifting. A backache can occur when one uses their back instead of their legs.
Smoking. Back pain is common among smokers. Secondhand smoke can lead to herniated disks because it prompts more coughing, which in turn can cause them. Smoking can increase the risk of osteoporosis by impeding blood flow to the spine.
Prevention
You can reduce back pain by getting into better physical condition and practicing good body mechanics.
To keep your back healthy and strong, do these exercises:
Exercise. You can build strength and endurance in your back by doing regular low-impact aerobic activities activities that don’t strain or jolt your back. Walking and swimming are excellent ways to spend time. Discuss your actions with your doctor and see what they recommend.
Increasing muscle strength and flexibility is good for you. These core strengthening exercises help to condition the abdominal and back muscles, resulting in the muscles working together as part of a natural corset for your back.
Maintain Healthy Weight. A heavyweight negatively affects the back muscles. To help prevent back pain, slim down if you’re overweight.
Reduce or stop smoking. People who smoke are at an increased risk of developing low back pain, for a given number of cigarettes smoked per day, the risk increases.